Since the First Industrial Revolution, each wave of innovation has transformed the world of manufacturing. From steam engines to automation, from assembly lines to robotics, the industry has continually reinvented itself to improve productivity, precision, and efficiency. This article explores the emergence of artificial intelligence within the framework of Industry 4.0.
Thanks to increasingly powerful algorithms and the use of real-time data, AI is disrupting production processes, redefining the roles of operators, and paving the way for new industrial models.
The industry has undergone several major transformations. In the 1970s, automation made it possible to standardize repetitive and strenuous tasks, delegating them to programmable machines (also known as Programmable Logic Controllers, or PLCs). In the 2000s, the introduction of sensors, industrial networks, and cloud computing marked the beginning of Industry 4.0, a connected industry where data became a critical resource.
It is within this context that AI is making its entry into the industrial world. Unlike traditional rule-based systems, artificial intelligence does not simply execute predefined instructions: it learns, analyzes, and predicts. It becomes a decision-support tool, capable of suggesting solutions, and in some cases, even implementing them automatically.
This evolution has been made possible by the growth of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), which enables the collection and centralization of massive amounts of data from production lines, equipment, operators, and control systems. AI leverages this wealth of data to train its models and deliver actionable insights aimed at optimizing industrial performance and enhancing safety.
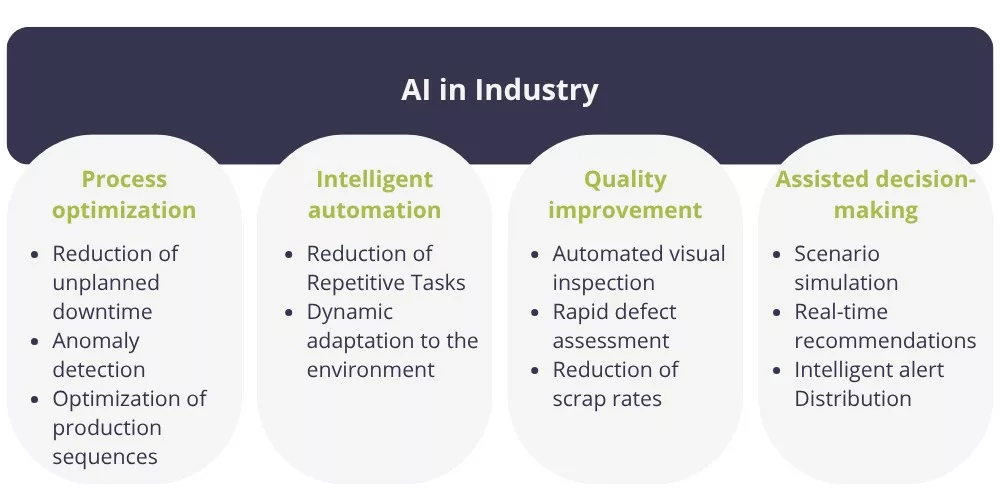
Artificial intelligence is not limited to one specific task. It plays a role at every stage of the production process (from planning to delivery) including manufacturing, quality control, and maintenance. Here are some common benefits of AI in industry:
On a bottling line, machine data analysis enabled the anticipation of certain technical failures. Information such as vibrations, temperature, energy consumption, and production speed was used to better understand equipment performance and detect early signs of wear.
Once this data was processed and made actionable, a relevant machine learning model was developed to more accurately estimate the remaining lifespan of machines and the likely causes of failure. The results were then integrated into the supervision system to allow for prompt handling of future malfunctions.
For example, it became possible to identify that a component of a filler was showing signs of fatigue, with an estimated two weeks remaining before failure. Similarly, the condition of a labeler on the line could be classified as critical, with only three days left due to motor overheating. This approach enables timely interventions, reduces costs associated with unexpected production stoppages, and allows for more efficient maintenance scheduling.
While the benefits of AI appear promising, several obstacles must be addressed to ensure successful implementation:
Artificial intelligence is establishing itself as a major driver of transformation in the industry. By combining the power of data with advanced analytical capabilities, it enables industries to meet increasing demands for performance. In modern production environments, AI plays a crucial role: it anticipates, learns, and recommends. Its impact is especially visible in control rooms and supervision systems. Where operators once had to process vast amounts of information, AI now acts as a true assistant capable of detecting deviations, simulating scenarios, and proposing decisions, all while adapting to real-time context.
At Motilde, by implementing efficient industrial data management, we harness artificial intelligence to support operators, turning their control rooms into genuine augmented decision centers.

Copyright © 2026. MOTILDE. All rights reserved.